Estimated Read Time: 49 Minutes
Updated: July 11, 2025
Table of Contents
When I was growing up, my parents used to say that you could never trust a mechanic; that a mechanic was always going to find something wrong with your vehicle, even when it was in prime operating condition. While that certainly wasn’t true, mechanics everywhere were painted with the same brush.
SEO is a very worthwhile endeavor for small businesses, but it has a similar reputation. I still hear stories from small business owners who have spent thousands of dollars and achieved nothing in terms of new business or improved rankings. While that situation continues to improve, there are still victims of SEO and digital marketing scams, and lingering myths and misconceptions that cause companies to hesitate or not risk another failed attempt at SEO and content marketing.
One of the best ways you can improve your chances of SEO success is by increasing your understanding of search. This post can help with that by providing a 30,000-foot view of how Google and SEO work. Like with the photo above, I’ll try to boil it down to the essentials—the land, sea, and air of SEO. It is intended as a guide for small business owners who want to determine whether an SEO company is doing busywork, harmful work, or work that will increase rankings and conversions.
The Purpose of SEO
Let’s start with the purpose of SEO.
Search engine optimization (SEO) is a continuous process that helps website owners improve their site’s visibility in search results. It eases search engines’ ability to find, rank, and share your content in search results and encourages audience engagement. In spite of its name, SEO isn’t about optimizing search engines; it’s about optimizing your website’s technical setup and content so search engines can easily find and understand it, and visitors leave satisfied and willing to advocate on your behalf.
SEO isn’t black magic or a trick. It’s hard work that involves every aspect of your website- the technical architecture, the content, and interactions that take place with and around your content. It ensures all components of your website work together, as intended, and in combination. To facilitate this, it’s best to take an early and holistic approach to SEO, one that bridges the gap between searchers and content providers while, at the same time, ensuring the entire user experience is cohesive, differentiated, and outstanding.

SEO bridges the gap between searchers and content providers. Photo by Chad Peltola on Unsplash
In the United States, you’ll find most small business SEO service providers focus their attention on the Google search engine. Google is, by far, the dominant player, often cited as commanding roughly 90% of the total search market. Remaining searches are done using artificial intelligence (AI) tools and country-specific search engines (like Baidu, Yandex, Naver, and Yahoo Japan) or specific Auto, Finance, Food, Entertainment, Shopping, and/or Sports sections of the Yahoo / Bing sites.
From a financial perspective, Google offers two types of search results: free and paid. Searchers pay nothing. Businesses have the choice of working on organic SEO, which helps them appear in free search results, or Google’s Pay-Per-Click (paid) advertising. Organic SEO tends to provide the best return on investment for small business owners and is the focus of this blog post.
Google’s Ranking Algorithm
So, how does Google decide what ranks where in search results?
Google uses a top-secret, artificially intelligent, and continuously updated collection of automated ranking algorithms. Results vary depending on the searcher, search location, search query, date and time, device and browser, and more.
Google’s ranking system is incredibly complex. It weighs hundreds of different ranking factors, including the words in the search query itself, the searcher’s location, settings, and search history, and the relevance, authority, quality, and usability of content it’s aware of on the Internet.
The words typed into Google’s search engine – the search query or SEO keywords – are the starting point for its ranking algorithm. But before Google begins the process of identifying potential search results, it first tries to establish what the searcher wants to accomplish with search results, in other words, their search intent.
Search Intent
Search intent refers to the why of a search query- why someone typed a query into a search engine and what they plan to do with the information provided.
Search intent is important because it helps search engines tailor their responses to match what users intend to do with that information. In doing so, search engines improve the value of search results and, ultimately, user satisfaction.

This is no simple process. Google must recognize the language being used and understand the searcher’s intent, even when there are misspellings, varied contexts, and different words and phrases used to refer to the same thing. It must discern when queries signal local intent, and when current events are influencing sought-after results. For example, a query for “pepperoni pizza” might signal the searcher wants to see recipes or nearby pizzerias. The query “doge” could represent the desire to learn more about the well-known American automobile brand (Dodge), the chief magistrate of Venice, or the US Department of Government Efficiency, a department only established in 2025.
In the end, Google wants to return the most relevant and valuable results possible. Search intent enables going beyond just trying to match words in a search query to words on a web page. By striving to decipher the underlying motivation behind a search query, Google can narrow and prioritize results that better align with the user’s goal. That also means, even if a page doesn’t exactly match a search query, it can still rank highly in search results so long as it fulfils the searcher’s underlying search intent.
Google Ranking Factors
Then the question becomes, with hundreds of billions of pages competing for visibility on the Internet, how does one ensure Google is aware of their website content, and that it ranks high enough to stand out in search results? This is where Google’s ranking factors come in.
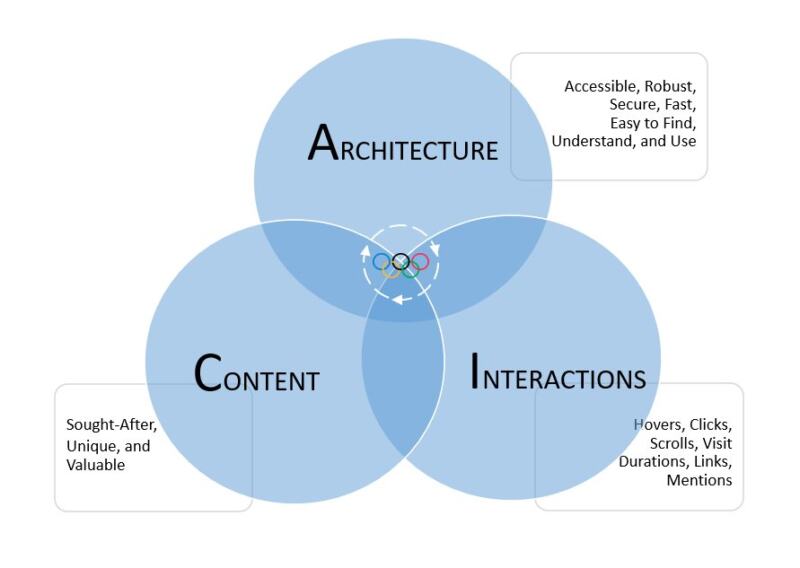
For ease of understanding, I have bundled the factors Google is believed to use when discovering and ranking search results into three interrelated groups:
- architecture;
- content; and
- interactions.
These labels are my own. I’ll explain what I mean by each of them below.
Architecture
Architecture refers to how your website has been designed and built. It encompasses all the structural and technical aspects of your website- hardware, software, security, structure, accessibility, rendering speed, and more.
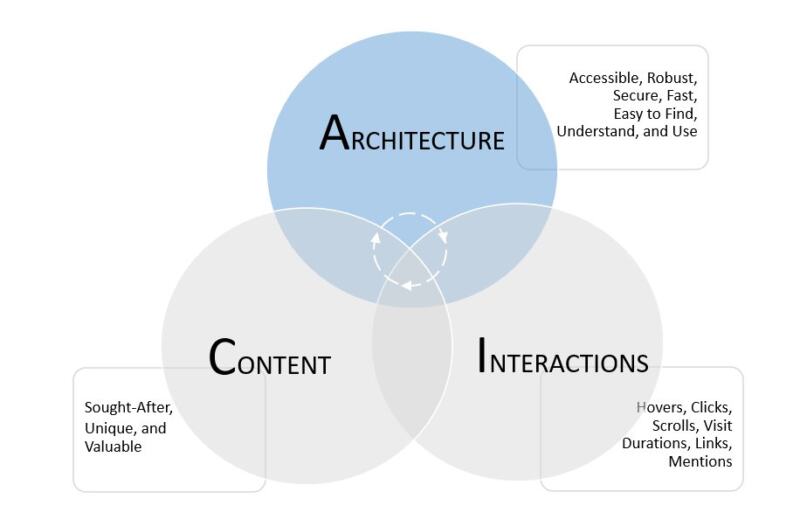
Architecture is important because Google’s search engine runs on a vast, global network of servers and data centers powered by software that communicates through various programming languages, operating systems, and network protocols. The system includes automated software programs called crawlers (spiders or bots) that explore the Internet and discover new and updated Web content. Crawlers follow strict protocols and policies when deciding what content to visit, assess, and store (index) for ranking purposes.
Remember I said Google only ranks content it’s aware of on the Web? Awareness depends on whether your content has been successfully crawled and indexed. To qualify for indexing, your site must follow Google’s technical guidelines and content policies, also known as Google Search Essentials or Google Webmaster Guidelines.
The technical design and build, or architecture, of your website is the first essential ingredient in this process. Website architecture ensures crawlers can discover, navigate, and correctly interpret information on your website. It facilitates understanding the relationship between various components and the quick and accurate rendering of them in search results.
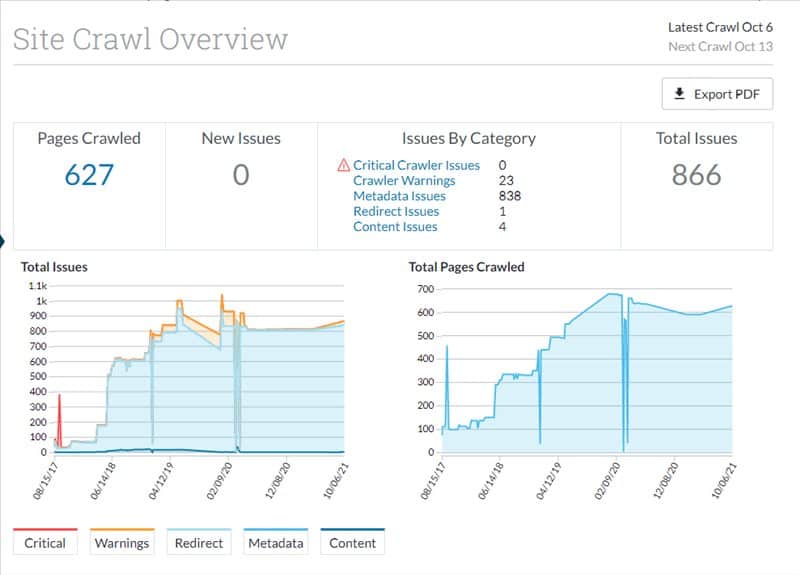
SEOs, web developers, and website owners should work proactively and collaboratively to ensure indexing success. There are SEO audit tools available on the market that can assist with this process. The tools help you identify, diagnose, and fix technical issues with your website. Bear in mind, you will still need SEO, web development, and website owner skills, knowledge, and experience to be able to interpret and act upon tool insights and recommendations appropriately.
If your content isn’t indexed, it won’t be ranked, and it won’t appear in search results.
Content
Now let’s move on to content.
Content includes all the digital information residing on your website. It includes web pages, blog posts, articles, news items, product descriptions, FAQs, PDFs, images, videos, and structured data.
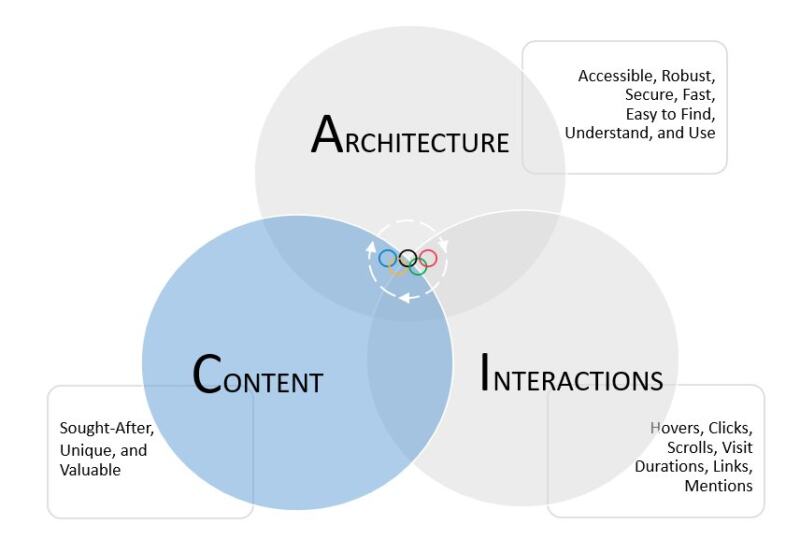
Once your website has been successfully discovered and crawled, the next hurdle is ensuring your content is considered unique and valuable, not just a repeat of everything that has already been published on the Internet. There are two reasons for this.
- First, Google will not index low-quality (thin) or duplicate content, including auto-generated or spammy content that offers minimal value to users. Essentially, if the content doesn’t “add anything” to the already existing Internet, Google will filter it out (ignore it).
- Second, it does not help your search audience, your SEO performance, or your online reputation.
Google Search Essentials will help you craft unique, high-quality content. In terms of ensuring the content you create is sought-after, start by identifying the words and phrases people use when searching for your goods and services. You can do that with an SEO practice called keyword research.
Keyword research helps small businesses learn what their target audience is searching for and develop content strategies to address their information wants and needs. It is a good way to begin to understand the competitive landscape and identify keywords for which they might have the potential to rank.
There are free and paid keyword research tools available on the marketplace. Most of the tool providers also provide free training videos.
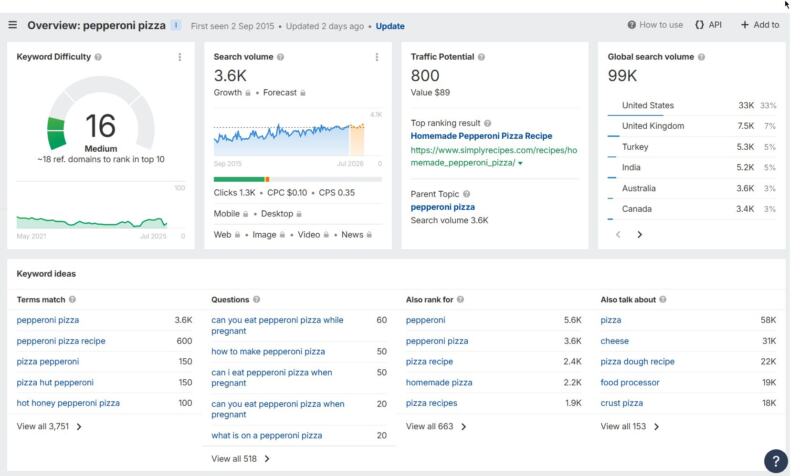
The tools take some time to get used to and master, so I suggest starting small, with the topics you and/or staff are most familiar with and being asked about all the time. Choose a seed keyword phrase with three or more words. Review matching terms and choose one that best aligns with what you have to offer, one with low volume and low competition. Write a blog post that satisfies what you think your intended audience plans to do with that information (their search intent), and add specific insights gained from your personal experience and expertise. (More on that in a minute.)
A caution about using AI-generated content. Whatever you choose to publish should be unique, accurate, and verifiable, including appropriately named and attributed sources. The information you derive from AI tools will be lacking in that it represents, at best, a polished consensus of whatever already exists on the Internet as of the date the AI tool was last trained. AI-generated content includes all the preexisting biases, errors, inaccuracies, and omissions you typically find on the Internet. The tools should, therefore, not replace your content creation efforts. They should supplement them and be reviewed to ensure appropriate depth, accuracy, and completeness.
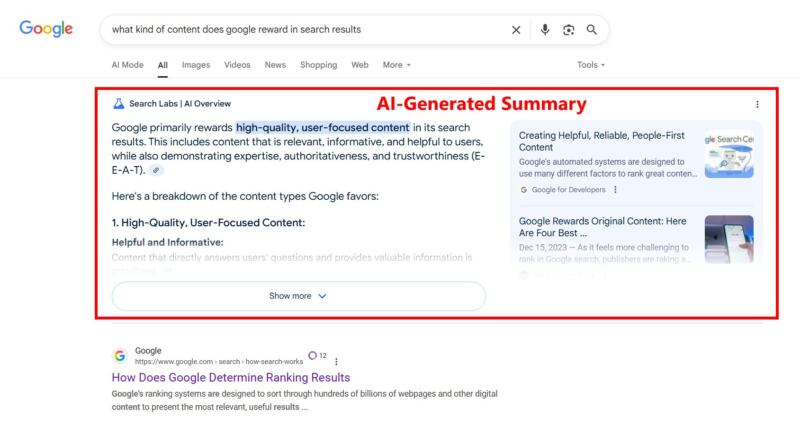
One last note, AI outputs also won’t include your specific expertise or experience. These elements afford maximum visibility by helping to boost your credibility, trust, and authority, key factors valued by both search engines and your target audience. They strengthen your content and enhance the overall user experience, thereby improving your chances of appearing in featured snippets, AI-generated search results (like shown above), and ranked search results.
Interactions
Your site is indexed.
Your content is relevant and high-quality.
Now you have to prove to Google that you deserve a high ranking by demonstrating third-party evidence that your content is valuable. That proof exists in the form of user interactions.
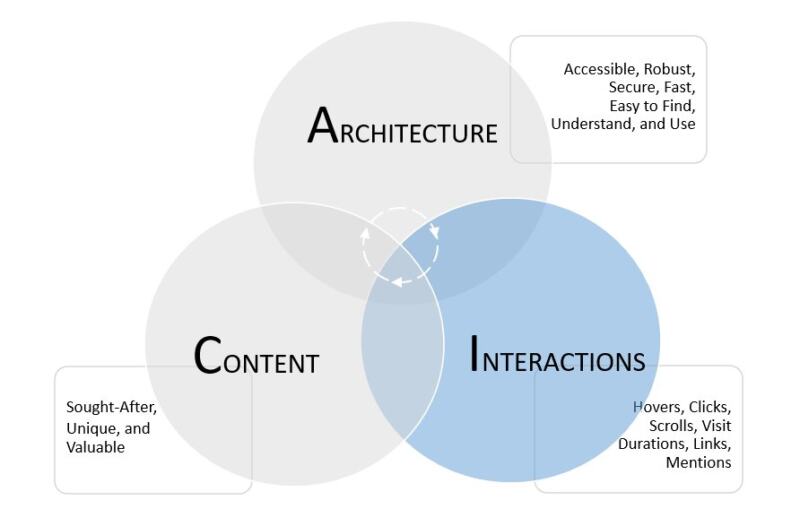
User interactions are the way users engage with your content. Positive user interactions, like hovering over or clicking on a search result, spending more time on one site versus another, and recommending content in the form of links and social mentions, are all powerful signs that your website offers engaging and valuable content. On-site navigation patterns (for example, the number of pages visited and how quickly it takes to navigate to them) also signal value and user satisfaction to search engines.
Links and online mentions are very important interactions involving your website and content. Links are clickable references to your content from an external source. Online mentions don’t link back to your website, but contain enough information for you to be recognized by search engines and human audiences. Links act like public endorsements, indicating a visitor found your content trustworthy and valuable enough to recommend it to their followers. Similarly, online mentions, especially those that are relevant, continue to increase in importance, especially with the rise of AI-driven search results.
It’s worthwhile noting that earning valuable backlinks and online mentions is the hardest part of SEO. You have to hang out in the same online venues as your target audience and become an active, contributing member. That is how you get exposed to, and earn the trust and respect of, audiences most likely to mention you online or link to your content from their own digital assets. Buying links is against Google’s link spam policy.
E-E-A-T and YMYL
I would be remiss if I did not mention E-E-A-T and YMYL. They, in addition to the previously mentioned Google Search Essentials, are critical considerations for Google’s ranking systems and guide how Google assesses the quality and credibility of websites and content, ultimately present content in search rankings.

Surgeon Demonstrating Expertise Sought By His Audience Medicalstudent1, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
EEAT stands for experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trust; YMYL stands for your money, your life. Both concepts were first introduced in 2014 and discussed in great detail in the Google Search Quality Rater Guidelines. They are intended to provide guidance when two or more pieces of content serve the same search intent. In them, Google emphasizes the credibility, quality, and reliability of content and the value of direct, personal involvement and insight, especially for sensitive (YMYL) topics in its ranking systems.
The takeaway is that you should adhere to E-E-A-T principles and ensure the accuracy and credibility of your content if you want to establish yourself as a valuable resource for users. It’s not enough for your content to serve a useful purpose. It must also demonstrate evidence of having come from an authoritative (respected, useful, and consistently high-quality) source, state verifiable and accurate facts, and exhibit trustworthiness with published privacy guidelines, terms of service, and an online reputation for protecting visitors and customers from harm.
Summary
Google dominates the US search market. Its purpose is to provide highly relevant, free, and helpful search results to its many audiences at no cost to the searcher. The service is funded by ad revenue—the money website owners pay to appear in sponsored search results.
SEO can help website owners increase their visibility in free search results by adhering to Google’s published policies and guidelines for technical, content, and link-building practices.
This post provides an easy-to-understand explanation of Google ranking processes and how SEO can help. It is intended as a guide for small business owners who want to determine whether an SEO company is doing busywork, harmful work, or work that will increase rankings and conversions.
My Dad was an airline mechanic, by the way. A very good one.





Leave A Comment